Cloud Computing Portability and Interoperability – Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a major development in information technology, comparable in importance with the mainframe, the minicomputer, the microprocessor, and the Internet. This chapter describes what makes it special.
The Cloud Concept
The essential concept of cloud computing is that IT resources are made available, within an environment that enables them to be used, via a communications network, as a service, as shown in Cloud Service.
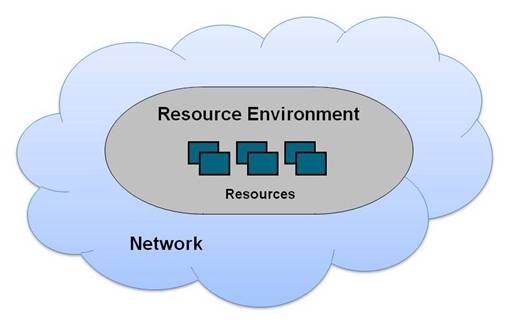
The resources can be raw computation resources, such as processing power and data storage, or computation resources that are programmed to perform a function, such as software development, web conferencing, or CRM.
The raw computation resources are real, but the environment often contains a virtualization layer, so that they are presented as virtual resources.
The environment enables managers to select, configure, and deploy the resources. For raw computation resources, the environment might, for example, enable a manager to select a virtual processor of a particular power, attach a chosen amount of virtual disc storage to it, and make it accessible at a particular IP address. For other resources the environment might enable a manager to define the number of users and the types of user that can use the resource.
The communications network is typically the public Internet or a private network that uses the Internet protocols (an intranet). The Internet protocols are the foundation of cloud interoperability and portability. Other kinds of network will not be considered in this Guide.
The Internet, and communications networks generally, are often represented by cloud shapes in figures and diagrams. This is what has given cloud computing its name.
The NIST Definition
The US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has developed a definition of cloud computing that is widely accepted within the industry, and is adopted by this Guide [NIST DEFINITION]. It includes:
- A description of the essential characteristics that a cloud service should have
- A primary classification of the ways in which a cloud service can be provided – its deployment models
- A primary classification of cloud services – its cloud service models
Essential Characteristics
A cloud service should have five essential characteristics:
- On-demand Self-service: Managers can obtain services as and when needed, without human intervention.
- Broad Network Access: Users can access services using a broad range of network client devices, such as browsers, mobile phones, tablets, laptops, and workstations.
- Resource Pooling: Resources are not dedicated to particular consumers but are pooled and allocated as required.
- Rapid Elasticity: The amount of resource allocated to a consumer can be expanded and contracted easily and quickly to meet demand.
- Measured Service: The amount of resource consumed is measured, to enable automatic expansion and contraction, and to give visibility of usage to providers and consumers.
Deployment Models
A cloud service may be deployed:
- As public cloud, by a cloud provider enterprise for use, often on commercial terms, by user enterprises
- As private cloud, by an enterprise for its own use
- As community cloud, by a collaborating group of enterprises for use by members of the group
- As hybrid cloud, where the user enterprise deploys a composite service whose components are a mixture of public, private, and community cloud services
Service Models
Three cloud computing service models are distinguished in the NIST definition, and they are a good basis for an analysis of portability and interoperability issues. They are Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
- For SaaS, the resources that are made available are software application programs, and the environment enables them to be configured and deployed.
- For PaaS, the resources are software application platforms, and the environment enables them to be configured and deployed, and enables applications to be created, configured, and deployed upon them.
- For IaaS, the resources are virtual processors and data stores, and the environment enables them to be configured and deployed, and enables platforms and applications to be configured and deployed upon them.
A further cloud service model is often included, though it is not part of the NIST definition: Business Process as a Service (BPaaS). In this model, the resources that are made available are systems that include people as well as IT components. They perform complete business functions, such as payment processing. They are available over the Internet, or an enterprise intranet, and exhibit the five essential cloud service characteristics.